Unprocessed Foods: Benefits, Lists & Smart Shopping Tips

Unprocessed Foods: Benefits, Lists & Smart Shopping Tips
Want a simpler path to weight control, steady energy, and long-term health? Center your diet on unprocessed foods. This guide explains what qualifies, why it matters, and exactly how to stock your kitchen so the numbers on your next BodySpec scan move in the right direction.
Quick-Glance Takeaways
- Unprocessed foods are items in their natural (or very lightly altered) state—think fresh produce, plain oats, or a raw chicken breast.
- Diets rich in unprocessed foods are linked to lower calorie intake, easier weight control, and reduced risk of chronic disease (a National Institutes of Health randomized trial).
- Use the NOVA food-processing scale (Group 1 = unprocessed → Group 4 = ultra-processed) to check where a food lands (Harvard Nutrition Source explainer).
- A simple rule of thumb: Short ingredient list made of recognizable foods = minimal processing. If a label lists only “almonds” or “whole oats,” you’re likely in Group 1.
Table of Contents
- What Counts as an Unprocessed Food?
- The NOVA Processing Scale Explained
- Science-Backed Benefits of Eating Unprocessed
- The Ultimate Unprocessed Foods List
- Label-Reading 101: Spotting Processed Imposters
- 5 Smart Shopping & Meal-Prep Strategies
- Sample One-Week Meal Plan Focused on Unprocessed Foods
- FAQ
- How BodySpec Can Help You Track Results
What Counts as an Unprocessed Food?
“Unprocessed” may sound black-and-white, but food processing exists on a spectrum. Most nutrition researchers reference the NOVA food classification, where Group 1 items are unprocessed or minimally processed (see Harvard’s overview):
- Fresh, frozen, or dried fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains (brown rice, rolled oats)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Nuts and seeds with no added oil or sugar
- Eggs, milk, plain yogurt
- Fresh meat, poultry, and seafood
These foods may be washed, chopped, pasteurized, or frozen, but none of those steps fundamentally change their nutritional blueprint.
Why “Minimally Processed” Still Counts
Cooking, freezing, or vacuum-packing are technically processing steps, yet they don’t add additives or strip away key nutrients. So go ahead and buy frozen berries—your smoothie will thank you.
The NOVA Processing Scale Explained
| NOVA Group | Description | Everyday Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Unprocessed or minimally processed | Fresh apples, dried kidney beans, steel-cut oats |
| Group 2 | Processed culinary ingredients (extracted from Group 1) | Olive oil, butter, salt, sugar |
| Group 3 | Processed foods (Group 1 + Group 2 ingredients) | Canned beans with salt, sourdough bread, cheese |
| Group 4 | Ultra-processed foods (industrial formulations with additives) | Soda, packaged cookies, flavored chips |

Science-Backed Benefits of Eating Unprocessed
1. Easier Weight Control
A two-week inpatient trial by the National Institutes of Health showed that participants consumed ≈500 extra calories per day and gained almost 2 lb on an ultra-processed menu, while losing nearly 2 lb on the unprocessed one (Hall et al., 2019).

2. Better Metabolic Markers
Large cohort studies report that replacing ultra-processed fare with minimally processed foods is linked to lower rates of type 2 diabetes and hypertension (NutriNet-Santé cohort).
3. Improved Satiety & Appetite Control
A systematic review found that fiber-rich whole foods increase fullness and reduce subsequent calorie intake.
4. Healthier Gut Microbiome
A review concluded that whole-food dietary patterns foster beneficial gut bacteria and reduce inflammation.
5. Lower Chronic Disease Risk
An umbrella review linked higher ultra-processed food intake with elevated risk of cardiovascular disease, depression, and all-cause mortality, while diets rich in unprocessed foods showed protective effects.
The Ultimate Unprocessed Foods List
Use this list as a quick reference during grocery trips.
Fruits & Vegetables
- Apples, berries, citrus, bananas
- Leafy greens, broccoli, peppers, carrots
- Frozen produce with no added sauces or sugar
Whole Grains

- Brown, black, or wild rice
- Quinoa, farro, barley, bulgur
- Old-fashioned or steel-cut oats
Legumes
- Black beans, chickpeas, lentils, split peas
Pro Tip: Canned beans move to NOVA Group 3 once salt is added, so choose dry or no-salt versions when possible.
Nuts & Seeds (Raw, Unsalted)

- Almonds, walnuts, pistachios
- Chia, flax, pumpkin seeds
Meat & Poultry
- Chicken and turkey (skinless for less saturated fat)
- Lean cuts of beef (e.g., sirloin, round roast)
- Pork tenderloin or chops (trim visible fat)
Fish & Seafood
- Wild salmon, cod, or halibut
- Shellfish like shrimp, mussels, scallops, and clams
Dairy & Eggs
- Plain, unsweetened yogurt or kefir
- 100% milk (dairy or fortified unsweetened plant milk)
- Eggs
Herbs, Spices, & Flavor Boosters
- Fresh herbs, dried spices, garlic, ginger
- Vinegar, citrus juice
For additional snack inspiration, explore our healthy, whole-food snack ideas.
Label-Reading 101: Spotting Processed Imposters
- Scan the ingredient list. If an ingredient list is excessively long, it’s a warning sign the food is highly processed.
- Look for “kitchen-friendly” words. Salt, vinegar, and whole spices are acceptable; sodium benzoate and Red #40 signal higher processing.
- Watch the sugar code names. Anything ending in “-ose” (fructose, dextrose) usually indicates added sugar.
- Check the fiber-to-carb ratio. Whole foods typically have ≥ 1 g of fiber for every 10 g of carbs.
- Additive red flags: emulsifiers (soy lecithin), artificial sweeteners (sucralose), flavor enhancers (MSG).
Need a deeper dive? Our guide on tracking macros effectively teaches you how to decode Nutrition Facts like a pro.
5 Smart Shopping & Meal-Prep Strategies
- Shop the perimeter first. Produce, meat, eggs, and dairy usually live around the edges of the store.
- Go frozen or canned (smartly). Frozen veggies keep nutrients; choose canned beans or tomatoes with no added salt.
- Batch-cook staples. Roast a sheet pan of veggies and cook a pot of quinoa on Sunday; mix and match all week.
- Seasonal swaps save money. Strawberries in summer, squash in fall—cheaper and tastier.
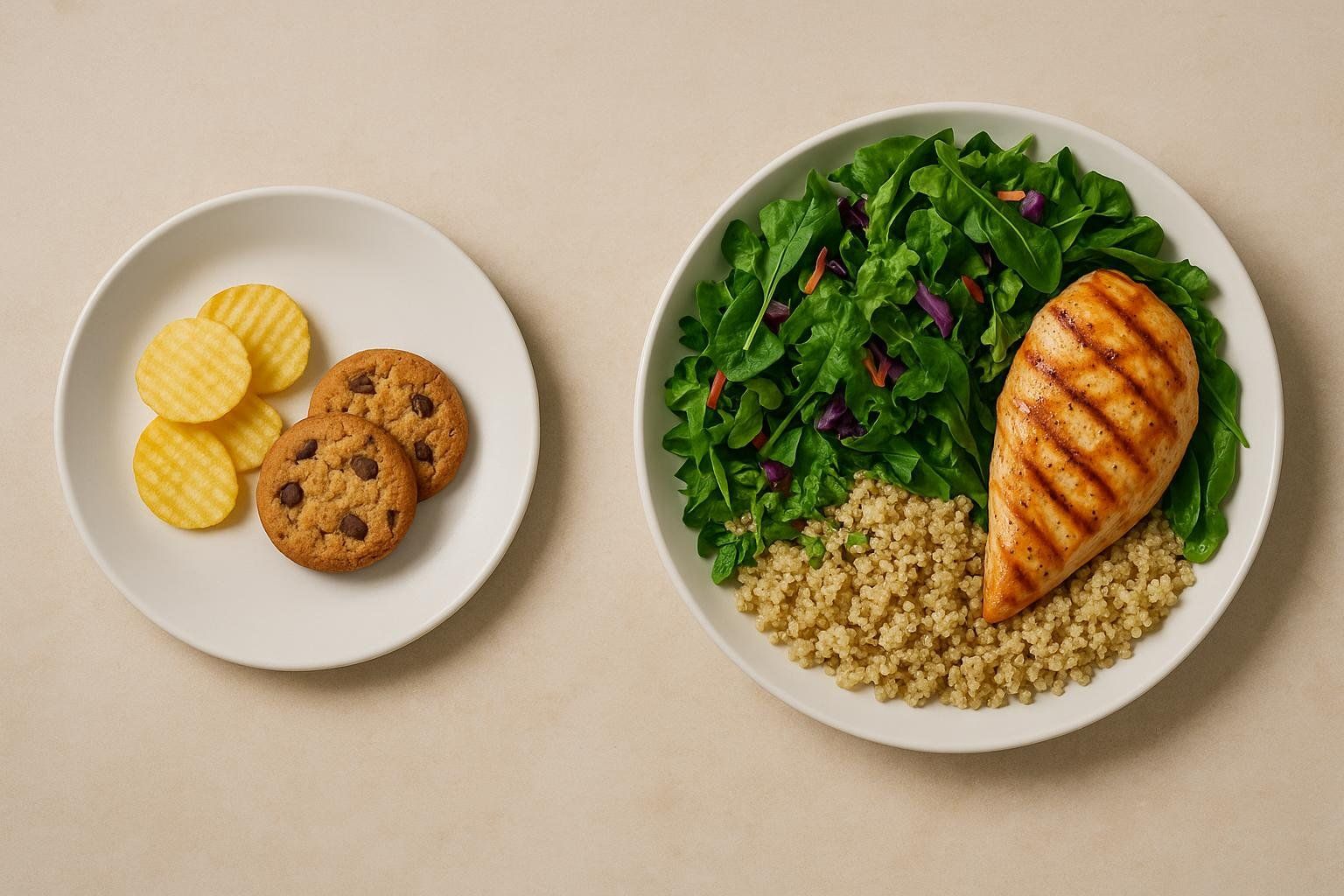
- Build balanced plates. Aim for ½ vegetables & fruit, ¼ protein, ¼ whole grains.
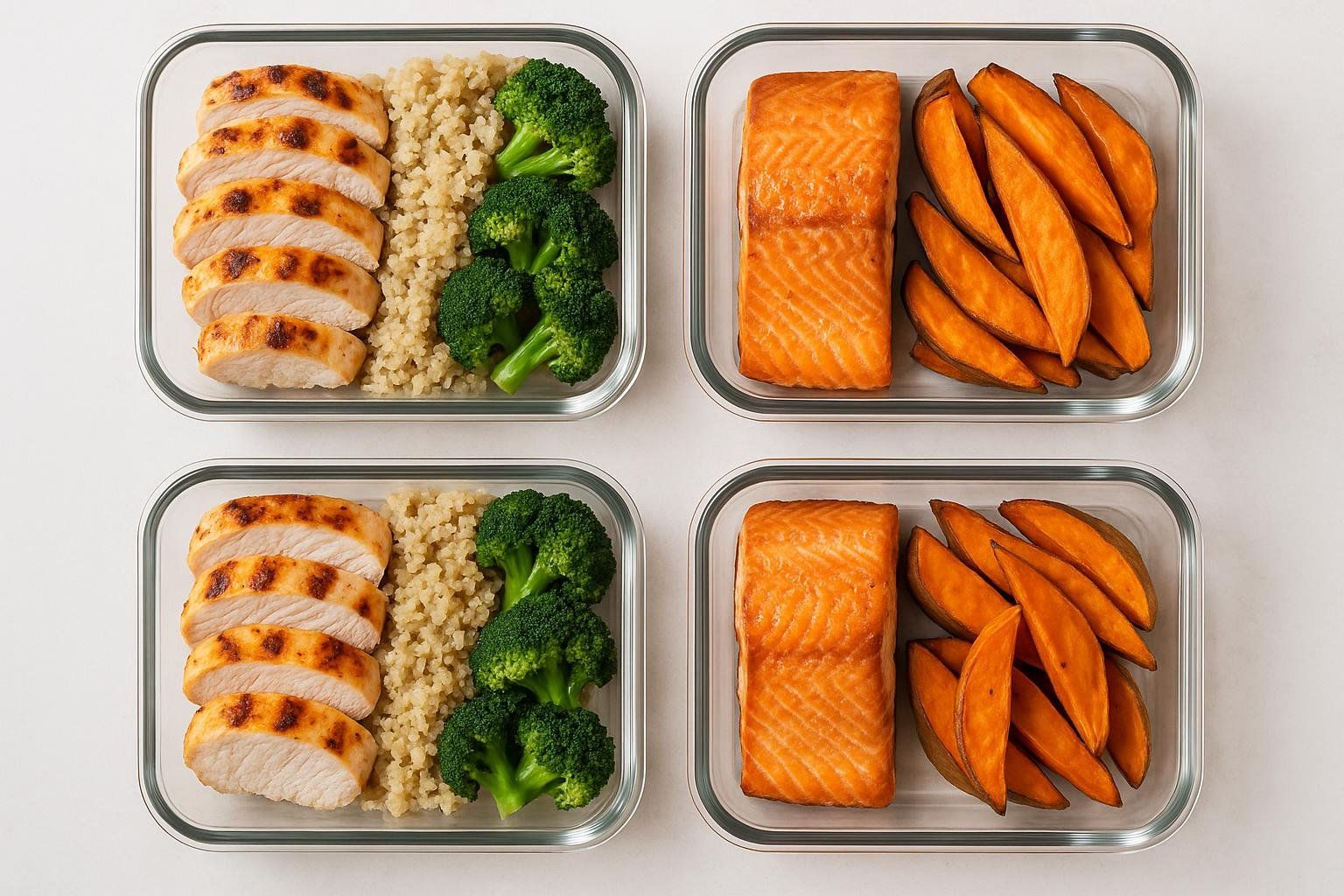

Sample One-Week Meal Plan Focused on Unprocessed Foods
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Snack | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mon | Overnight oats with berries & chia | Quinoa–chickpea salad with mixed veggies | Apple & raw almonds | Grilled salmon, sweet potato, steamed broccoli |
| Tue | Greek yogurt with banana & walnuts | Turkey lettuce wraps with avocado & tomato | Unsalted roasted chickpeas | Lentil–vegetable soup |
| Wed | Veggie omelet (spinach & tomatoes) | Tuna and avocado bowl with brown rice | Carrot sticks & edamame | Tofu stir-fry with mixed veggies & brown rice |
| Thu | Green smoothie (spinach, banana, oats) | Kale salad with black beans & roasted sweet potato | Pear & pumpkin seeds | Baked chicken thighs, quinoa, green beans |
| Fri | Steel-cut oats with flax & blueberries | Leftover chicken–quinoa bowl | Plain yogurt with berries | Shrimp with cauliflower “rice” & sautéed peppers |
| Sat | Scrambled eggs, avocado, mushrooms | Lentil power bowl with roasted cauliflower & beets | Trail mix (raw nuts + unsweetened dried fruit) | Grass-fed steak, roasted potatoes, garden salad |
| Sun | Fruit salad with unsweetened kefir | Wild rice & salmon bowl with steamed asparagus | Peach slices & raw pistachios | Sheet-pan cod, broccoli, wild rice |
FAQ
Is frozen produce considered unprocessed?
Yes—if it’s just the fruit or vegetable with no added sauces or sugar, it remains “minimally processed.”
How many unprocessed meals should I aim for?
Research suggests that health risks are more likely when ultra-processed foods contribute more than about 20–30% of daily calories (Global Food Research Program fact sheet). Building your meals primarily from unprocessed foods is a practical strategy for staying within this healthy range.
Are canned beans okay?
Absolutely. Choose no-salt versions, rinse before eating, and you’re good to go.
Does coffee count?
Black coffee is minimally processed (roasted beans and hot water). A sugar-loaded frappuccino, however, is a Group 4 dessert in disguise.
How BodySpec Can Help You Track Results
Swapping boxed meals for real foods can reshape your body composition—but only if you can measure it. A BodySpec DEXA scan provides:
- Visceral fat score: Diets high in ultra-processed foods are linked to increased visceral fat (cross-sectional MRI study); track improvements as you eat cleaner.
- Lean mass tracking: Ensure weight loss comes from fat, not muscle.
- Bone density: Whole-food diets rich in calcium and magnesium help keep bones strong.
Book a scan at one of our mobile locations and watch your dietary changes appear in clear, data-driven numbers.
The Bottom Line
Unprocessed foods are a straightforward route to better health. Start small: add one new Group 1 item to every meal this week. Your waistline, energy levels, and BodySpec results will thank you.